Portfolio
Our portfolio is a result of high-throuput screening of a diverse library containing lead-like and drug-like compounds to discover small molecule inhibitors of accumulation of insoluble glycogen or polyglucosan bodies, using an APBD patient skin fibroblast cell-based assay. As all Glycogen Storage Diseases (GSDs) share the etiology of excessive normal or malconstructed glycogen, we believe that APBD represents a prototypical GSD and thus development of pharmaceutical inhibitors of glycogen accumulation is likely to benefit most GSDs.
Ex-vivo High-Throughput Screening
- Cell-based assay to detect inhibition of polyglucosan accumulation with library of small molecules.
- Assay readout: Amylase-resistant fluorescence of Periodic Acid Schiff’s reagent (PAS) staining.
- Use of APBD patient derived fibroblasts for screening Software-based analysis of cell images.
- Focus on ADMET-compatible (novel and ‘lead-like’) compounds.
APBD patient fibroblasts
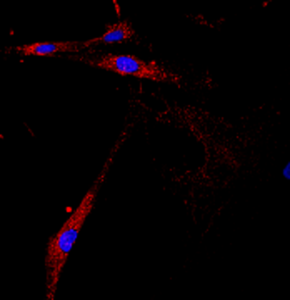
Solmesky et al (2017)
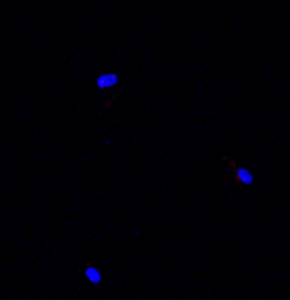
Healthy control fibroblasts
The selected compounds were further investigated in vitro and in vivo.
In an APBD mouse model (Gbeys/ys), our lead compound, GHF-201 (Compound A), was effective in lowering polyglucosan bodies, improving motility and , carbohydrate burn and lifespan extension.
Furthermore, our extensive cell and in vitro analyses show that GHF-201 targets the lysosomal protein LAMP1 and enhances autophagic flux as well as respiratory and glycolytic ATP production, transforming the adversely excessive glycogen into a useful fuel source.
First In Human – GHF-201 was approved for an Urgent Compassionate Use program in Israel limited to 3 APBD patients.
GHF partnered with LDS to formulate GHF-201 in a highly-bioavailable non-aqueous oral solution, to be administered daily.
The program, led by Prof. Alexander Lossos and his team at Hadassah University Hospital–Ein Kerem, Jerusalem, Israel, enrolled 3 APBD patients, totaling over 8 patient-years, and has shown promising clinical improvements.
The growing knowledge and evidence about GHF-201 suggest that it may offers a new, safe, and efficacious approach to treat APBD and additional glycogen and lysosomal storage disorders, as well as diseases with greater prevalence.
Research and Development
GHF-201 reduces glycogen in target organs of APBD mouse*
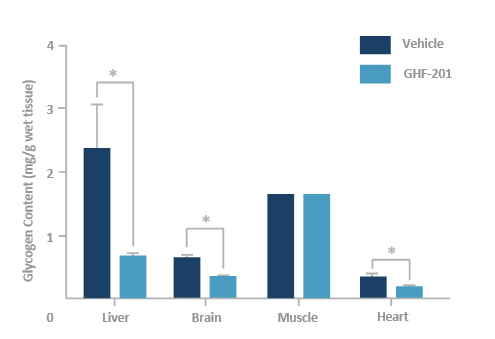
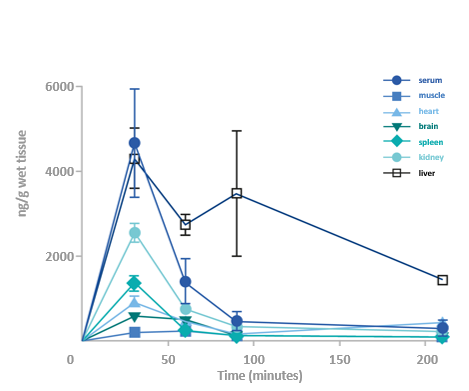
*Homozygous for the human mutated GBE gene Gbeys/ys
GHF-201 improves motility in APBD mouse*


*Homozygous for the human mutated GBE gene Gbeys/ys
GHF-201 extends survival in the APBD mouse*
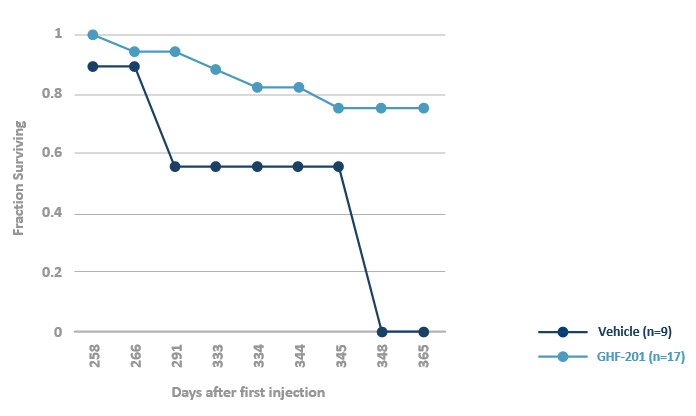
*Homozygous for the human mutated GBE gene Gbeys/ys
Vaknin et al, 2021
GHF-201 Mechanism of Action is Known*
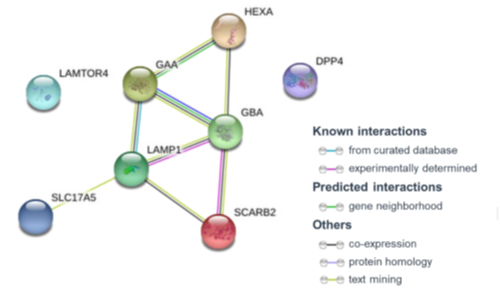
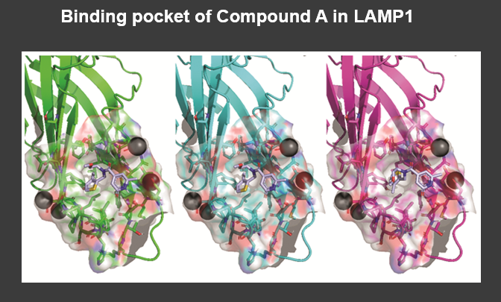
GHF-201 modulates lysosomal and autophagy genes
LAMP1 has a pivotal role in lysosome integrity and function
*Determined by NPOT technology
Vaknin et al, 2021
GHF-201 Mechanism of Action is Known*
- GHF-201 is a novel compound capable of degrading polyglucans and over-accumulated glycogen
- In vivo proof of concept for use of GHF-201 in treating APBD and other glycogen storage disorders
- GHF-201 activates auto-lysosomal catabolism
- Potential to treat lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs), such as Mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I) and Gaucher disease
- GHF-201 reduces nuclear & cellular levels of glycogen
Publications

EMBO Molecular Medicine 13: e14554 | 2021

Biochem J. 2017 Sep 28;474(20):3403-3420. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170469.

Journal of Lipid Research Volume 58, 2017




