Conditions
GHF motivation is focused on developing a treatment for Adult Polyglucosan Body Disease (APBD). Using our scientific expertise and collaborations we aim to characterize each compound in our portfolio and to leverage our compounds mechanism of action to reach more disorders with similar pathologies. The encouraging effect of GHF-201 on lysosomal activity motivates us to further develop it as a potential treatment for other disorders, beyond APBD. So far, we found promising results in other Glycogen Storage Disorders (GSDs), and Lysosomal Storage Disorders (LSDs).
APBD
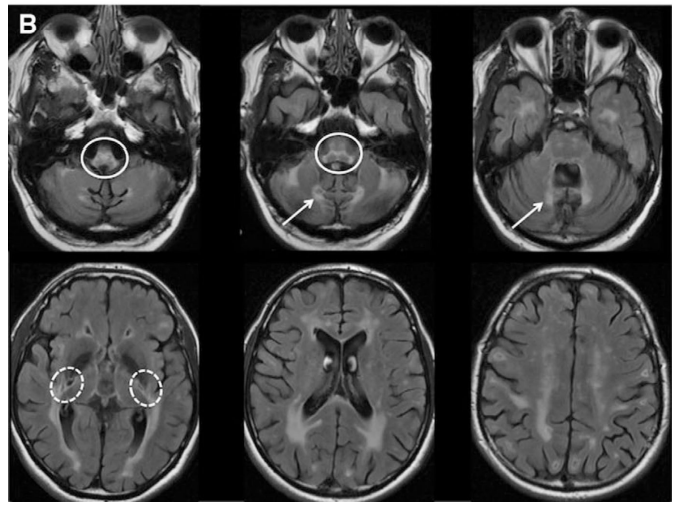
- APBD is a GSD caused by glycogen branching enzyme (GBE) deficiency leading to poorly branched glycogen, called polyglucosan, which precipitate, aggregate, and accumulate into polyglucosan bodies. (Akman et al, 2009; Mochel et al, 2012)
- APBD is affected by mutations in the same gene as Andersen’s disease (GSD type IV) which is characterized by the absence of GBE, this may lead to liver failure and death in childhood. Milder mutations of GBE, as in APBD, lead to smaller polyglucosan bodies, these do not disturb most cell types. In neurons and astrocytes, however, over time polyglucosan bodies plug the tight confines of axons and processes and lead to APBD (Akman et al, 2015)
- Unlike Andersen’s disease, the onset of APBD is at late stage of adult life, where patients become symptomatic.
- APBD presents with symptoms similar to more common diseases such as, Multiple Sclerosis, hereditary spastic paraplegia, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, adrenomyeloneuropathy, prostate hypertrophy in men, MSA and ALS, this results in a difficult patient journey with misdiagnoses along the way.(Hellmann et al, 2015; Schwartz et al, 2020)
- Although there are about 300 confirmed APBD cases worldwide, this is likely an underestimation. Recent publications suggested that the number of APBD patients is more likely to be 10-folds higher. (Koch et al. 2025).
- The majority of APBD patients are Ashkenazi Jewish.
Mochel et al.(2012). Glycogen metabolism and glycogen storage disorders. Annals of Neurology
GHF is currently perusing the development of GHF-201 as the first approved treatment for APBD. Following promising outcomes from an ongoing urgent compassionate use program and a phase I study in healthy volunteers that is nearing completion, we are now heading towards a clinical study involving APBD patients.
GSDs
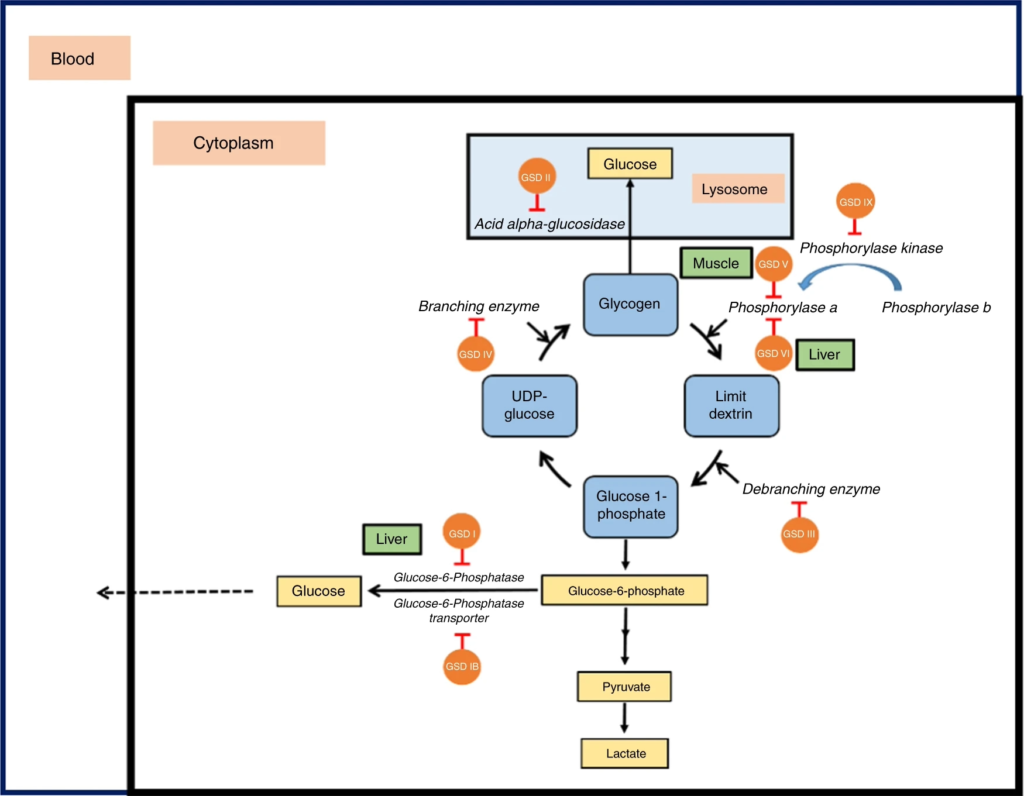
- GSDs are a group of inherited rare metabolic disorders caused by mutations that affect the break down or synthesis of glycogen. (Molares et al, 2021; Ellingwood et al., 2018)
- These disorders are characterized by many metabolic symptoms in patients, such as- hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, muscle weakness and more.
- Unfortunately, treatments are limited and are mostly dependent on nutritional management which may hold off some of the symptoms but in the long run the disease may prevail. One exclusion is GSD2 (Pompe), a Lysosomal glycogen storage disorder with an approved enzyme replacement therapy. (Corbett et al, 2025)
- The general incidence of GSDs is around 1- 20,000, but could be higher in specific population such as Ashkenazi Jewish people. (Gümüş et al, 2023)
-Kanungo et al. (2018). Glycogen metabolism and glycogen storage disorders. Annals Of Translational Medicine
LSDs
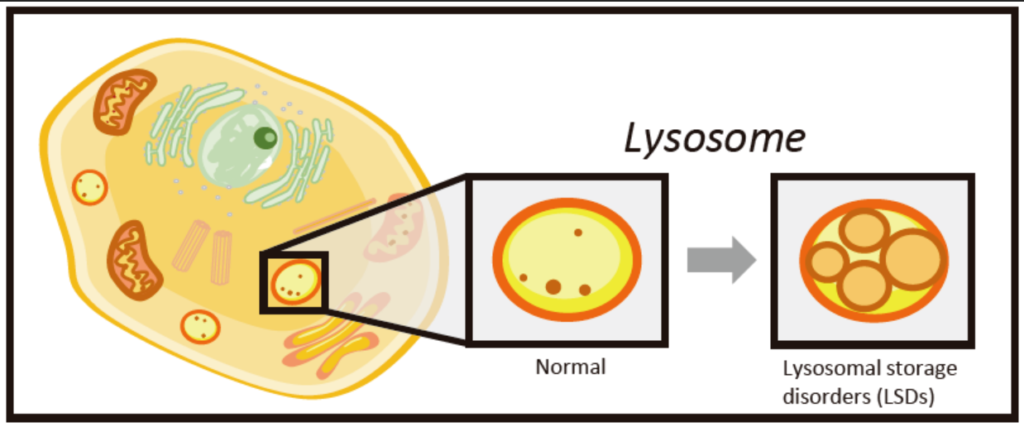
- LSDs are a group of rare inherited conditions characterized by deficiencies in enzymes required by lysosomes, leading to accumulation of cargo in lysosomes, eventually creating a toxic environment in cells. (Platt et al, 2018)
- LSDs are categorized by the substance that accumulates in lysosomes, such as glycogen in GSD2 (Pompe) or lipids in Gaucher disease.
- LSDs may affect many different organs, such as the liver, muscles, heart and brain, all of which can lead to various clinical outcomes that may include- developmental delays, organ enlargement, skeletal issues, neurological problems, cardiac disease and more.
- Current available treatments aim to slow progression and manage symptoms. Most common treatments include enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) or substrate reduction therapy, In addition to nutritional support and management.
- The general incidence for LSD is around 1 in 5,000 to 10,000.
Our lead candidate, GHF-201 was found to interact with the lysosomal protein LAMP1 and through that to increase lysosomal activity, this intriguing mechanism of action along with promising initial results in GSD2 (Pompe) mouse model and cells alludes to the potential of GHF-201 as a future treatment for LSDs in general and GSD2 (Pompe) specifically.
Mashima et al. (2020). Biomarkers for Lysosomal Storage Disorders with an Emphasis on Mass Spectrometry. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,
Neurodegenerative disease
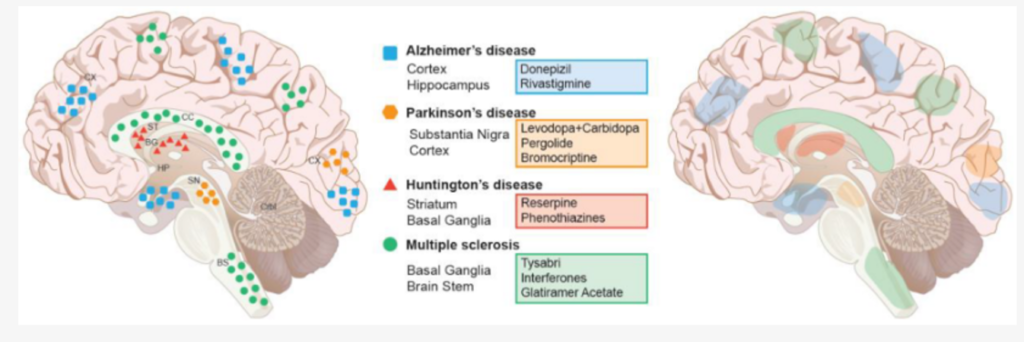
- Neurodegenerative diseases are defined as conditions where nerve cells gradually lose function and die, common examples include- Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, ALS and Huntington’s. (Lamptey et al, 2022)
- These diseases often involve abnormal protein buildup, caused by mutations in specific genes or other risk factors such as age.
- Symptoms can include memory loss, movement problems, and general cognitive decline.
- Most neurodegenerative diseases currently lack effective cures.
Many Neurodegenerative diseases are characterized by protein accumulation and cellular toxicity as a result of defective cellular protein degradation; this leads to protein aggregates in organelles such as lysosomes. The mechanism of action of our glycogen reducing compounds, such as lysosomal activity enhancement by GHF-201 can be used to complement other developed therapies for neurodegenerative diseases in the future. Supporting this notion, Initial studies performed on skin cells from neurogenerative disorders and neurogenerative disorders cell lines showed an increase in autophagy and cellular energy levels.